Patient misidentification cases are persistent as no industry-wide solution exists

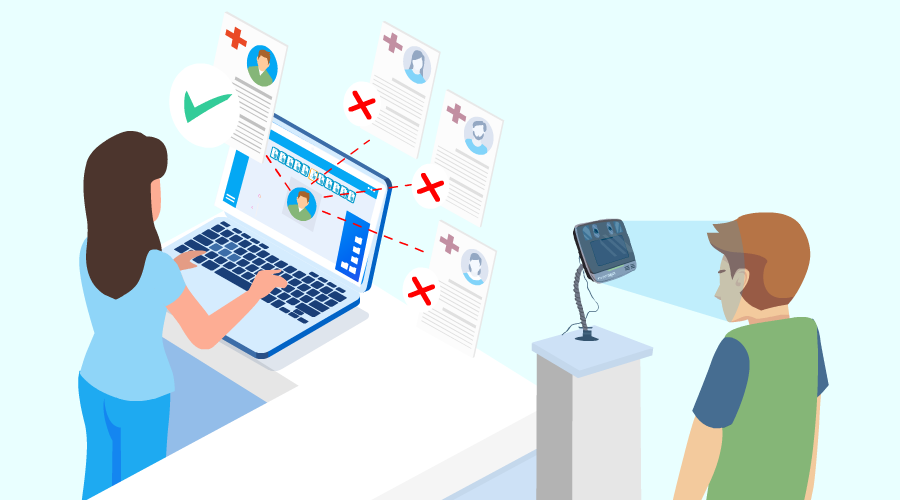
Synchronizing medical information with the appropriate patients accordingly – how hard can it be, right? Well, it is precisely the opposite. It is easier said than done – patient misidentification cases are abundant. Since the introduction of electronic health records (EHRs), people thought that it would make the lives of everyone involved easier, but the reverse has happened. EHRs are filled with issues like misspellings, incomplete data, common names, outdated addresses, and so on, which overall leads to duplication of records. One of the consequences of all of this, according to a reputed organization, is the match rates being an average of 80%, sometimes even lower. It doesn’t sound all that bad, but it is the result obtained from the same healthcare provider the records have been created in!
One out of every five patients is likely to suffer from patient identification errors and become one of the many patient misidentification cases in the US. This is not the only problem, however. Patient matching errors are like a web created by spiders – trapping all the parties who are connected to patient identification – patients, healthcare providers, physicians, insurance companies, and so on.
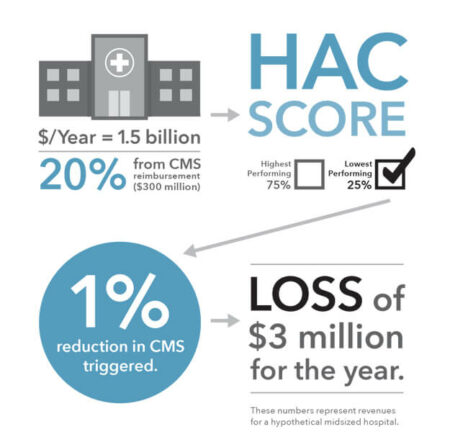
Patient misidentification cases are also synonymous with rising costs as patient misidentification is famous for being a persistent multibillion-dollar problem in the healthcare industry. A patient matching error costs a hospital around $2000, and if we look at the bigger picture, there are $1.5 million of denied claims for a single hospital in a given year. That is an outrageous amount of money which is completely wasted due to these errors.
As per the definition, patient matching refers to obtaining the accurate medical record for a given patient whenever necessary, to make informed decisions regarding the health of the patient. Healthcare professionals are frustrated that this is not what they experience whenever they are matching the patients with their records and are clamoring for something which will change the industry and generate accurate patient identification – something RightPatient is very good at doing.
Let’s explore more in-depth into why patient matching errors occur. Patient matching is also reliant on the hospital employees who come into contact with it – they need to fill in the gaps for the new data, or else they might need to update changes in data like a surname, address, etc. to ensure accuracy. However, errors, in this case, maybe made by either the patient, the staff, or both. A patient might not be attentive and may not check whether accurate data has been entered; likewise, an employee may not check with the patient to ensure he has put in the correct data or not. They might think that it is not a big deal, but there lies the problem. Such inconsistencies which they believe are inconsequential lead to increased waiting times, worse patient outcomes, financial losses, wrong treatments, and sometimes even result in deaths.
A reputed individual in the industry stated that to combat these errors, a lot of countries have switched to unique IDs for patients. Sadly, the US is not doing that yet, as it has no nationwide standardized patient identifier nor any effective strategy to do so. Thus, the responsibility is pushed onto the shoulders of the healthcare providers, each coming up with their own approach for identifying patients.
A lot of suggestions have been made by experts to solve these errors, like software for patient identification, improvements in data standards, and ID cards, among many other options. However, the only one which is being pursued by many and used by early adopters are biometric patient identification systems. RightPatient is the most appropriate choice to eliminate patient matching errors. It uses iris scanning to ensure that the correct patient is identified, and it does so with ease, as reported by over a hundred healthcare providers who are using it. As it is using iris scanning, it is also hygienic and safe, as it requires no physical contact, and is convenient for the patients, as all they need to do is look into the scanner to match with their records. Since it is also less time consuming than traditional patient matching, it is lauded by many for improving the patient experience as well as patient safety. Patient matching has never been easier and more accurate, according to the users of RightPatient.