Physician Burnout is a Multi-billion Dollar Problem – How Are You Solving it?

Well, the cat’s out of the bag now. EHR (electronic health record) systems are not only causing problems for patients, insurance companies, and healthcare providers, but also among another critical player in the healthcare industry – the physicians. According to new research, this new problem – physician burnouts – are associated with EHR systems, and causes losses starting from $2 billion to an outrageous $6 billion annually. That is an obscene amount of money lost. Moreover, the researchers also gave an estimated amount of $4 billion lost due to lower productivity, physician turnovers, as well as other aspects relevant to burnout.

Other findings of the research demonstrate that a single physician employed by the healthcare provider generates an estimated amount of $7,000 in burnout costs per year for the hospital. However, that is an average estimate, as the cost can be as low as almost $4,000 and can go up to $11,000, depending on the severity of the issues they face due to the burnout.
It can be seen quite clearly as to how the physicians are being affected adversely due to these burnouts – reduced work-life balance, reduced wellbeing, tremendous workloads, which ultimately lead to more mediocre quality of healthcare for the patients, thus, a loss for everyone concerned. However, the holistic view of the economic problems physician burnouts can cause is yet to be seen.
But what is burnout? It is pent-up stress which is built over time and creates a sense of physical and mental tiredness, low levels of accomplishments, and monotony – all of which is generated from a lot of work-related factors, primarily EHR related ones.
Thanks to this research, it is now known that not only do burnouts cause damages to physicians and patients, but also the healthcare providers’ financials. According to the researchers, the study did not consider indirect burnout related costs like reputational damage, disruption, and so on – the costs which added up to $4 billion are directly related to physician burnouts.
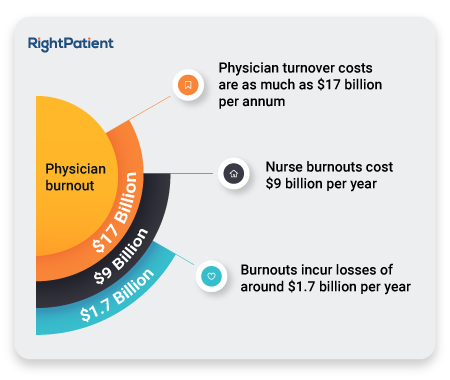
However, a positive thing which can be taken away from this study is that the estimated figure it gave is quite lower than previously conducted studies. A 2018 report claimed that burnouts incur losses of around $1.7 billion per year, physician turnover costs are as much as $17 billion per annum, while nurse burnouts cost $9 billion per year.
Industry pundits estimate that almost half of the physicians suffer burnouts, with an AMA study claiming that 44% of physicians suffered from at least one symptom of burnout in 2017. Another aspect is physician burnouts influence some individuals more than the rest, citing that females are more likely to face burnouts as well as those individuals who are at larger, more prominent health systems since they face more pressure.
But why are the physicians facing such burnouts? Most physicians have reported that they have to click through the EHR interface thousands of times every day, going through several layers of EHRs, searching for patient data and matching them with the patients instead of focusing on the patients themselves and providing the services they signed up for. Thus, the immense pressure they face, especially if they are from larger, more complex health systems, as well as administrative tasks, all contribute towards physician burnouts and hampers patient care as well as the healthcare industry as a whole.
How does RightPatient fit here? Well, it matches the patients with their electronic health records, so that the physicians do not have to. RightPatient is a biometric patient identification system which uses iris scanning to detect the patients and match them with their proper EHR. Patient matching has never been easier, as all the patient needs to do is to look at the camera, and they are identified quickly. RightPatient integrates seamlessly with major EHR systems and thus is used by over a hundred health systems, effectively combating physician burnouts. It also reduces patient matching errors as well as enhances patient safety and reduces losses caused by burnouts as well as identification errors, as reported by its users.






















