Patient safety issues occur due to patient misidentifications

When electronic health records (EHRs) were introduced, people lauded it as the next big thing in the technological landscape of the healthcare industry. There were many reasons – it was entirely digital as the name suggests, could be accessed quickly and whenever required, reduced paperwork, among many other reasons. However, once it was widely implemented, the reality was drastically different. Instead of solving these problems, EHRs added additional ones along the way – patient safety issues.

EHRs have created many problems for patients and healthcare providers alike. They have created risks which were unpredicted at the time of their implementation, which can potentially generate the chance to make grave errors in the treatment processes for patients, specifically if the treatment involves medicines. If this seems terrible, it gets even worse. These problems associated with EHRs are much more catastrophic for children and younger patients since their prescribed drugs are age-based. A study has found that EHRs do not take age into account; thus, it does not tackle the problems associated in a pediatric environment. Other than that, patient safety issues like matching errors are synonymous with EHRs. This is where biometric patient identification systems like RightPatient come into play.
The problems healthcare providers face while using EHRs lead to misidentifications mostly. Some of the challenges EHR users face are:
- Problems associated with displaying patient information, or incomplete/corrupt patient data
- Issues related to patient data entries which cause delays
- Problems with EHRs regarding feedback or notifications
- Disruption in the workflow if data needs to be shared
So what are the actual problems associated with patient safety issues caused by EHRs?
Restricted information results in wrong medications
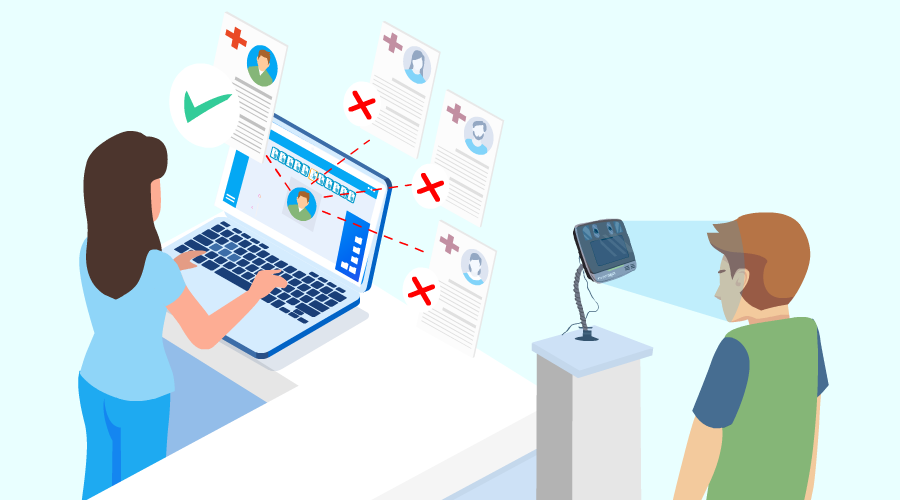
EHRs usually provide the hospitals with blank data fields which the latter can fill in, if required, regarding making notes making it easier for colleagues. However, they do not know whether their colleagues have access to those specific fields, which can create many problems. For example, if a doctor had made a note within the EHR regarding the medical condition of a patient, say glucose level, the nurse who will administer the medication may not be able to view this note because her access is restricted, not taking into account the medical condition. Such problems lead to a lot of medical complications. Likewise, if required fields are not available to be viewed by everyone in the hospital, the staff may get confused between patients with common characteristics like name, address, etc., causing patient matching errors.
A patient is provided with excess or wrong medication due to an entry error
This is the primary cause of confusing units – between imperial units and metric units. Thus, as it is common in the US to use pounds, and if the weight is entered in pounds, but the EHR accepts only kilograms, this will hamper with the medication. Medications are sometimes dependant on the weight, especially in the cases of children, and they may, unfortunately, receive larger doses of medicine than required, which can be fatal. Other than that, if a patient is misidentified, then this will cause the patient to receive the wrong medication as well.
Missed doses of medications occur due to problematic information displays
EHRs can usually list all the medicines that have been scheduled for patients, along with the time and dosage required. However, sometimes due to patient matching errors, they may end up with the medicines planned for some other patient, and this can be fatal for both the patients involved if someone is not cautious enough while administering the medications.
Duplicate patient IDs are created
By far, one of the most significant flaws of EHRs is consistent to this very day. News regarding patient matching errors are very common, and at least one person you know has faced it. How does it happen? Very simply – once a patient comes in and a hospital representative does not find the individual’s record in the EHR, the employee tries to save time by creating a new ID instead of searching more in-depth for the correct record. The staff thinks that this is the way to save time and effort but generates another source for losses by the employer. Sometimes even the patients are to be blamed – if they are not attentive enough while verification, the hospital staff may pick the wrong record for them. Its effects can range from being financial losses to even life-threatening. Due to this single issue, everyone involved with healthcare has suffered – patients, healthcare providers, insurance companies, and so on. Healthcare companies are now clamoring for a unique patient ID solution to eliminate these errors.
Medical ID thefts take place
Another consequence of patient safety issues via EHRs – fraudulent activities. Addicts and professional thieves can very easily misuse others’ IDs and gain access to healthcare benefits or drugs which are entitled to the actual patients, resulting in financial losses incurred by the unfortunate patients. All this happens because there was no sure way to identify whether the medical record belonged to the perpetrator, until now.
What can be the solution to patient safety issues?
As seen from the problems, all of them point in one direction – patient matching errors. From all of this, patient identification error is seen as a disease in itself of the healthcare industry. Everyone involved is affected and suffers due to it in various ways and degrees. It is a multibillion-dollar problem in the US, where fixing a single entry costs from $1000-5000.
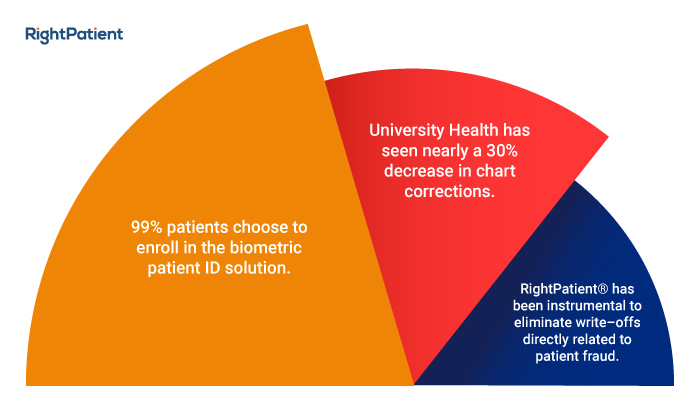
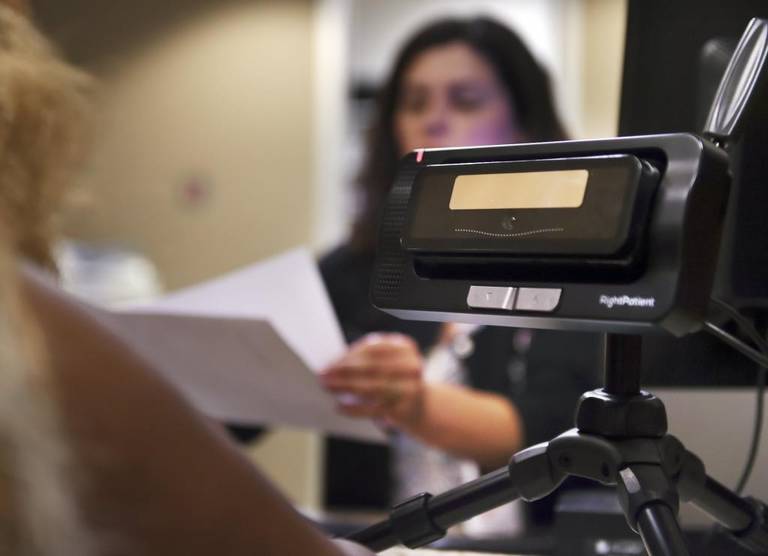
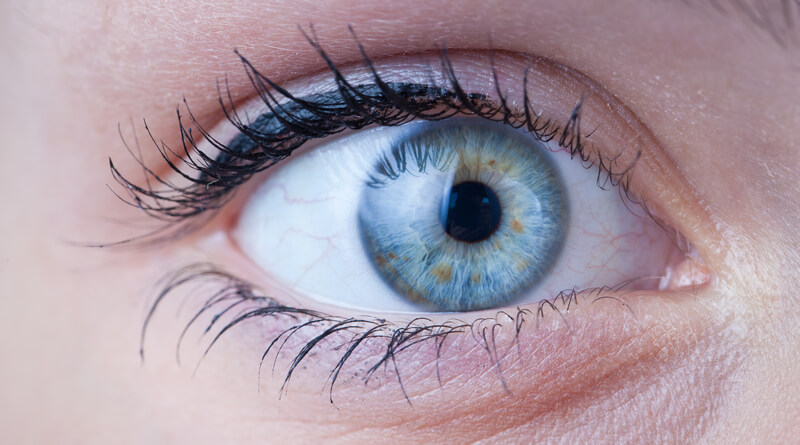
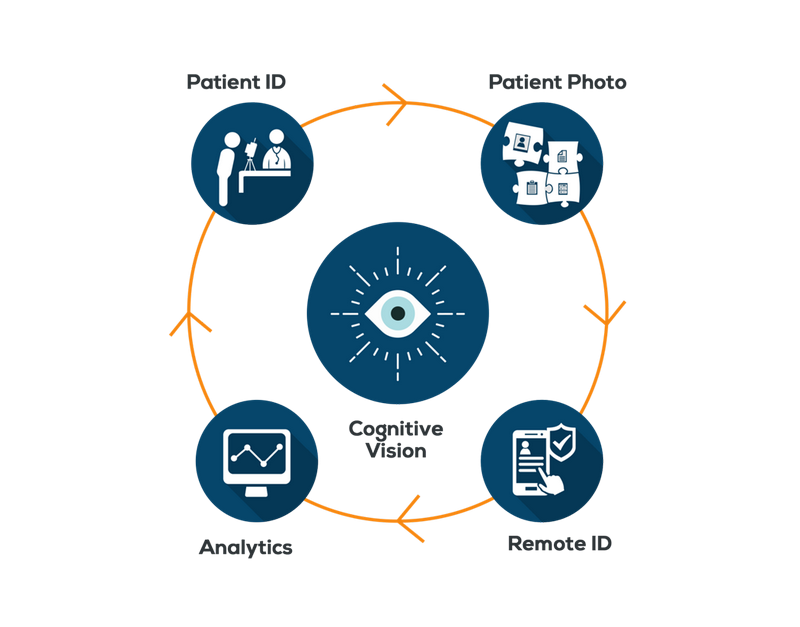
However, its days are numbered, it seems, as biometric patient identification systems like RightPatient are successfully eliminating it from the healthcare providers who use it. It uses iris scanning, which is easy and convenient for patients – all they need to do is look into the camera, and they are identified accurately. Another benefit of this biometric modality is that it also correctly identifies the irises of the younger patients as irises are formed within ten months of birth and remain unchanged. Patients also love it because there is no chance of getting any contagious diseases as it does not require physical touch. Over a hundred healthcare providers are using it, and they are reiterating the same thing – patient experience has improved along with patient safety due to the reduction of errors and the speed of the process.
















 Brad Marshall is an Enterprise Development Consultant with RightPatient®. With several years of experience implementing both large and small scale biometric patient identification projects in healthcare, Brad works closely with key hospital executives and front line staff to ensure project success.
Brad Marshall is an Enterprise Development Consultant with RightPatient®. With several years of experience implementing both large and small scale biometric patient identification projects in healthcare, Brad works closely with key hospital executives and front line staff to ensure project success.