The Importance of Maintaining Patient Data Integrity

The following guest post on patient data integrity in healthcare was submitted by Gabriel Tedde Cabot.
While all physicians, care providers and practices understand the importance of keeping accurate files and records for maintaining patient data integrity, the unique challenges and concerns of a digital file system may pose a greater risk than many practitioners might realize. From the struggle to keep patient records coherent and to maintain unified files across multiple applications and programs to the issues that may be caused by a data breach, today’s practices would be wise to assess the effectiveness of their records and data processes. Loss of data integrity may result in any number of potentially serious consequences, ranging from HIPPA violations to compromised patient care.

Patient data integrity is important to maintain in healthcare. Learn more about how to protect it in the evolving world of digital healthcare.
Creating and Maintaining the Right Digital Infrastructure
The first step towards ensuring digital information can be created, stored and accessed with greater accuracy is also one of the most important. Creating and maintaining the right digital infrastructure can streamline all processes that may involve patient records and ensure that inconsistencies within a file system are less likely to occur. Applications that can be linked more easily and databases that provide cross-platform support are often crucial assets for reducing errors, oversights and optimizing the efficiency of staff and associates.
The Importance of Staff and Employee Training
Having the right digital working environment is only one step in the process for ensuring more effective and accurate record-keeping, one that may be of little practical benefit when employees are not properly trained. Properly training all employees who access or use database systems, patient records and similar applications can help to minimize problems caused by user error. Assessing the current skill level, understanding and overall computer literacy of existing staff can also be quite helpful in identifying any areas that may require attention or improvement.
Failing to provide ongoing training for their staff is a mistake common to both small practices and larger facilities. Updated software, the addition of new applications and changes to the daily operational process of a clinic, practice or healthcare facility often entails the need to train and educate employees who may not yet be comfortable or even familiar with new systems or tasks. Ongoing training also provides a chance for associates to brush up on any skills or concepts that may have gone unused for too long.
Performing Periodic Assessments or Audits to Ensure Accuracy
Quality assurance can go a long way, both towards ensuring that established resources and operational processes are being utilized correctly and for identifying smaller issues before they have a chance to grow into larger and more serious problems. Assessing the accuracy of past records and ensuring that patient data integrity is being maintained effectively is not a concern that should be left to chance. Further assessments should also be performed whenever new operational policies go into effect or when changes are made to the software, systems and applications used by employees.
Protecting Patient Information in the Digital Age
From instituting a more effective password policy to utilizing secure virtual data rooms, there are numerous ways for organisations to ensure all patient data and information is able to be kept safe and secure. Damage caused by unauthorized access to data, files and electronic information may be considerable and practitioners who fail to make online security a priority may be placing themselves and their patients at greater risk of breach or other security issue. Malware or unauthorized users who are able to gain access to electronic records may result in the loss of vital data or files and records that no longer be considered secure.
While even basic measures to enhance digital security can make a considerable difference, more effective may be achieved by organisations who elect to make use of the right resources. Contracting with third-party IT department or security specialist may provide a more cost effective solution for smaller practices that lack the financial resources needed to expand their staff. Investing in secure virtual data rooms used to store and distribute information in a safer manner can also ensure that medical organisations are not placing patient data or information at greater risk. Finding and selecting the services, resources and solutions that make it possible to reduce or even eliminate many of the most common and costly digital security risks is always a worthwhile undertaking.
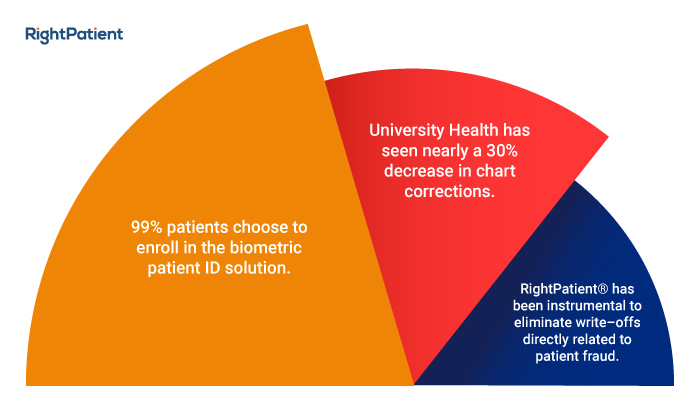
An effective way of ensuring patient data integrity is by using solutions that protect patient data by preventing medical identity theft, duplicate records, and mix-ups. Solutions like RightPatient do so by ensuring accurate patient identification across the continuum of care. By ensuring that the accurate medical records are identified every time patients use healthcare services, mix-ups and duplicates are prevented easily. Moreover, it prevents medical identity theft in real-time by verifying patients’ identities using their faces. Several healthcare providers are already benefiting from using the platform and are maintaining patient data integrity.
Staying Up to Date With Changing Technology and Emerging Trends
With new applications, digital services and innovations continuing to shape and change the industry, practitioners and medical organizations can no longer afford to fall behind the times. Failing to learn more about new potential security risks or electing to overlook the latest security resources and solutions could prove to be nothing short of a disaster. When it comes to maintaining patient data integrity, staying up to date with the latest technology or learning more about the most recent threats and security concerns is of paramount importance.
Gabriel Cabot is a digital marketing strategist from London who enjoys reading, writing and learning about new technologies, programming, health and the Internet.







 Brad Marshall is an Enterprise Development Consultant with RightPatient®. With several years of experience implementing both large and small scale biometric patient identification projects in healthcare, Brad works closely with key hospital executives and front line staff to ensure project success.
Brad Marshall is an Enterprise Development Consultant with RightPatient®. With several years of experience implementing both large and small scale biometric patient identification projects in healthcare, Brad works closely with key hospital executives and front line staff to ensure project success.


 Michael Trader is President and Co-Founder of RightPatient®. Michael is responsible for overseeing business development and marketing activities, government outreach, and for providing senior leadership on business and policy issues.
Michael Trader is President and Co-Founder of RightPatient®. Michael is responsible for overseeing business development and marketing activities, government outreach, and for providing senior leadership on business and policy issues.