Hospitals Might Lose $323 Billion – Reduce Yours by Ensuring Patient Data Security

Healthcare around the world has been arguably facing one of its biggest challenges yet, and the US healthcare system is no exception to the effects of the coronavirus pandemic. While there are spikes in COVID-19 cases, things are looking quite bleak for the financial performance of hospitals this year. To be exact, over a staggering $323 billion could be lost only in 2020! Is there any solution to mitigate the losses? RightPatient might be the answer – as it ensures patient data security and prevents medical identity theft in real-time. Let’s explore.

Unimaginable hospital losses
It is quite simple – due to the pandemic, hospitals had to focus more on the overwhelming number of COVID-19 patients, and thus, stopped treating regular patients. While this was expected, the financial losses are still huge.
According to the American Hospital Association, healthcare providers have reported declines of 34.5% in outpatient volume and 1.5% in inpatient volume, on average. Projected losses for the duration of March–June 2020 have been around $202 billion. Moving forward, the AHA estimates that the second half of 2020 will incur a loss of around $120.5 billion for providers – leading to an unprecedented sum of $323 billion in losses for the year 2020. However, the AHA does warn that this might be an understatement – the numbers might go even higher.
Providers do not expect losses to reduce for the rest of the year either. The AHA’s president has even stated that the US healthcare system is facing the biggest financial crisis in its history due to the pandemic as well as reduced patient numbers.
While the US federal government has provided over $170 billion as emergency funding for the providers, many fear that it might not be enough to overcome the heavy losses.
Medical identity theft is on the rise
 While COVID-19 and its long-lasting effects are raging on, that has not stopped hackers from attempting to steal sensitive patient data through healthcare data breaches. Security experts have stated that there is a huge opportunity for hackers to steal patient data since it is rich with valuables like Social Security numbers, insurance information, and so on. Moreover, they can sell patient records for up to $1000.
While COVID-19 and its long-lasting effects are raging on, that has not stopped hackers from attempting to steal sensitive patient data through healthcare data breaches. Security experts have stated that there is a huge opportunity for hackers to steal patient data since it is rich with valuables like Social Security numbers, insurance information, and so on. Moreover, they can sell patient records for up to $1000.
Healthcare in the US is expensive, and that is the reason why medical identity theft is so common. Fraudsters simply buy the patient data from the black market, and do not need to worry about any more healthcare expenses – the fraudulent bills are passed on to the shoulders of the victims. As can be seen, ensuring patient data security is quite important.
Medical identity theft not only hampers the patients financially – it affects patient safety as well. When a fraudster uses the patient data to gain access to healthcare services such as expensive procedures, medications, and equipment, their data is recorded into the victims’ patient records. Thus, the patients might further suffer from incorrect medications and procedures based on an altered medical history, making patient data security a topmost priority, even during the pandemic.
Ensure patient data security with RightPatient
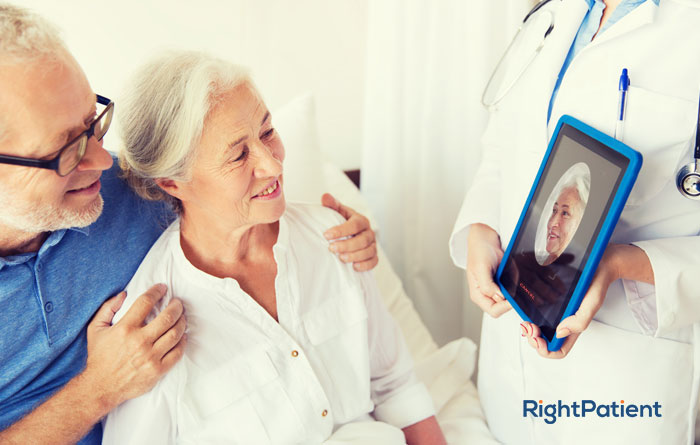
RightPatient has been protecting millions of patient records for leading healthcare providers for years. It is a touchless biometric patient identification platform that locks the medical records of the patients with their photos upon registration. After enrollment, all the patients need to do is look at the camera and the platform matches the photos and provides the correct patient record within seconds. Thus, if a fraudster comes by, he/she will be red-flagged, preventing medical identity theft.
Moreover, due to the pandemic, patient identification in hospitals needs to be upgraded to a touchless platform like RightPatient to prevent infection control issues and enhance patient safety. RightPatient meets all the requirements for any given health system or hospital by preventing medical identity theft, ensuring patient data security, enhancing patient safety, and preventing duplicate record creation, boosting the bottom lines. Reduce your losses by using RightPatient and protecting patient records now.